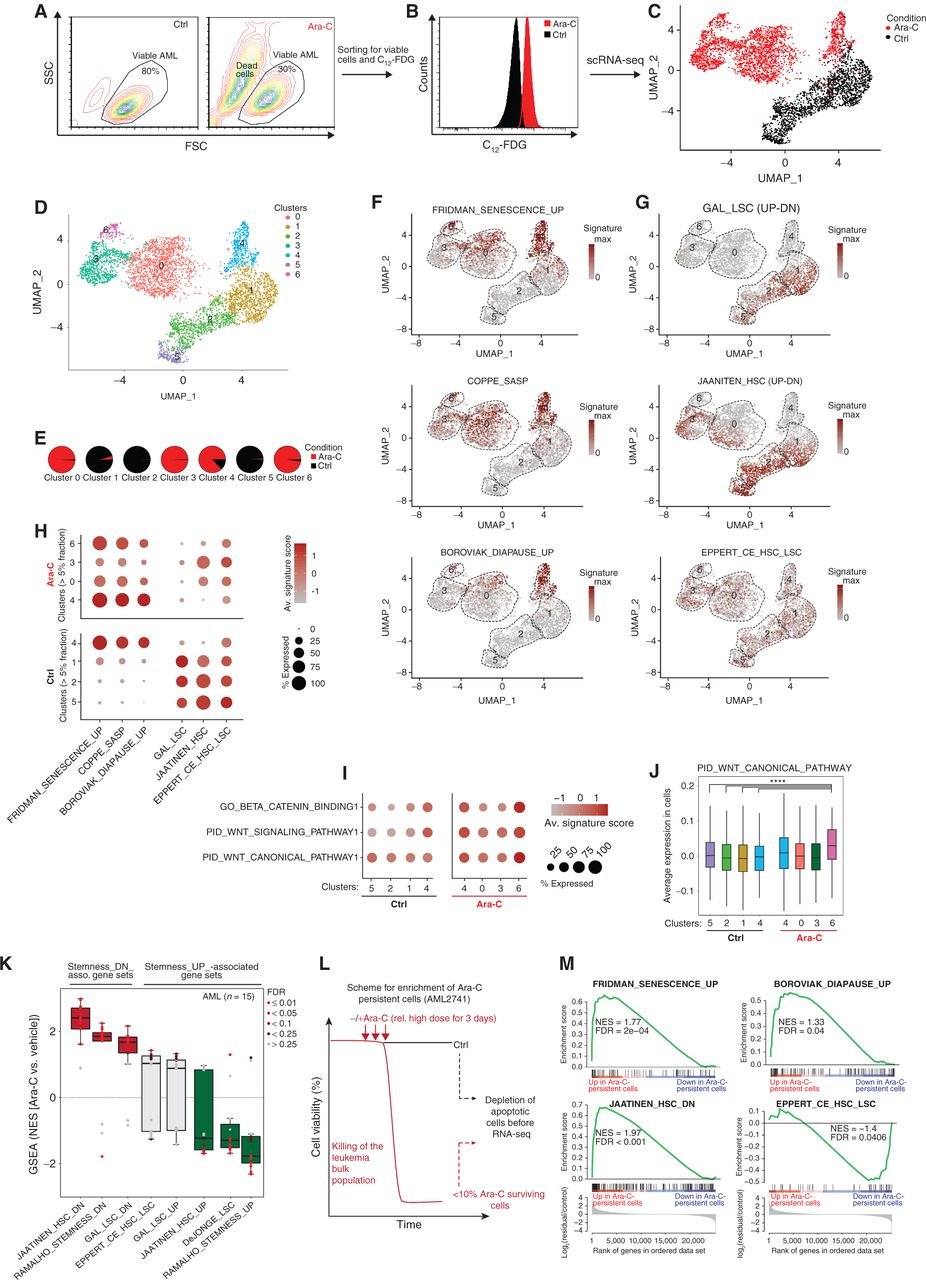
Chemotherapy Induces Senescence-Like Resilient Cells Capable of Initiating AML Recurrence
Patients with acute myeloid leukemia (AML) frequently relapse after chemotherapy, yet the mechanism by which AML reemerges is not fully understood. Herein, we show that primary AML cells enter a senescence-like phenotype following chemotherapy in vitro and in vivo. This is accompanied by induction of senescence/inflammatory and embryonic diapause transcriptional programs, with downregulation of MYC and leukemia stem cell genes. Single-cell RNA sequencing suggested depletion of leukemia stem cells in vitro and in vivo, and enrichment for subpopulations with distinct senescence-like cells. This senescence effect was transient and conferred superior colony-forming and engraftment potential. Entry into this senescence-like phenotype was dependent on ATR, and persistence of AML cells was severely impaired by ATR inhibitors. Altogether, we propose that AML relapse is facilitated by a senescence-like resilience phenotype that occurs regardless of their stem cell status. Upon recovery, these post-senescence AML cells give rise to relapsed AMLs with increased stem cell potential. SIGNIFICANCE: Despite entering complete remission after chemotherapy, relapse occurs in many patients with AML. Thus, there is an urgent need to understand the relapse mechanism in AML and the development of targeted treatments to improve outcome. Here, we identified a senescence-like resilience phenotype through which AML cells can survive and repopulate leukemia.
Journal: Cancer Discovery PMID: 33500244 DOI: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-20-1375

TBL1XR1 Mutations Drive Extranodal Lymphoma by Inducing a Pro-tumorigenic Memory Fate
The most aggressive B cell lymphomas frequently manifest extranodal distribution and carry somatic mutations in the poorly characterized gene TBL1XR1. Here, we show that TBL1XR1 mutations skew the humoral immune response toward generating abnormal immature memory B cells (MB), while impairing plasma cell differentiation. At the molecular level, TBL1XR1 mutants co-opt SMRT/HDAC3 repressor complexes toward binding the MB cell transcription factor (TF) BACH2 at the expense of the germinal center (GC) TF BCL6, leading to pre-memory transcriptional reprogramming and cell-fate bias. Upon antigen recall, TBL1XR1 mutant MB cells fail to differentiate into plasma cells and instead preferentially reenter new GC reactions, providing evidence for a cyclic reentry lymphomagenesis mechanism. Ultimately, TBL1XR1 alterations lead to a striking extranodal immunoblastic lymphoma phenotype that mimics the human disease. Both human and murine lymphomas feature expanded MB-like cell populations, consistent with a MB-cell origin and delineating an unforeseen pathway for malignant transformation of the immune system.
Journal: Cell PMID: 32619424 DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2020.05.049

Rational Targeting of Cooperating Layers of the Epigenome Yields Enhanced Therapeutic Efficacy against AML
Disruption of epigenetic regulation is a hallmark of acute myeloid leukemia (AML), but epigenetic therapy is complicated by the complexity of the epigenome. Herein, we developed a long-term primary AML ex vivo platform to determine whether targeting different epigenetic layers with 5-azacytidine and LSD1 inhibitors would yield improved efficacy. This combination was most effective in TET2mut AML, where it extinguished leukemia stem cells and particularly induced genes with both LSD1-bound enhancers and cytosine-methylated promoters. Functional studies indicated that derepression of genes such as GATA2 contributes to drug efficacy. Mechanistically, combination therapy increased enhancer–promoter looping and chromatin-activating marks at the GATA2 locus. CRISPRi of the LSD1-bound enhancer in patient-derived TET2mut AML was associated with dampening of therapeutic GATA2 induction. TET2 knockdown in human hematopoietic stem/progenitor cells induced loss of enhancer 5-hydroxymethylation and facilitated LSD1-mediated enhancer inactivation. Our data provide a basis for rational targeting of cooperating aberrant promoter and enhancer epigenetic marks driven by mutant epigenetic modifiers.
Journal: Cancer Discovery PMID: 31076479 DOI: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-19-0106
