Unique Immune Cell Coactivators Specify Locus Control Region Function and Cell Stage
Chu, C. S., Hellmuth, J. C., Singh, R., Ying, H. Y., Skrabanek, L., Teater, M. R., Doane, A. S., Elemento, O., Melnick, A. M., & Roeder, R. G. (2020). Unique Immune Cell Coactivators Specify Locus Control Region Function and Cell Stage. Molecular cell, 80(5), 845–861.e10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2020.10.036
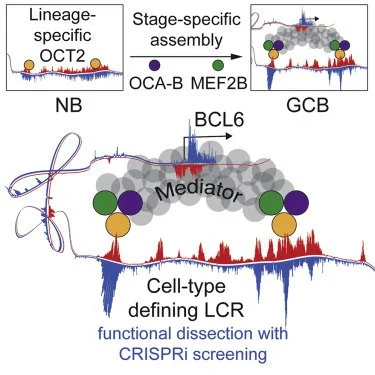
Locus control region (LCR) functions define cellular identity and have critical roles in diseases such as cancer, although the hierarchy of structural components and associated factors that drive functionality are incompletely understood. Here we show that OCA-B, a B cell-specific coactivator essential for germinal center (GC) formation, forms a ternary complex with the lymphoid-enriched OCT2 and GC-specific MEF2B transcription factors and that this complex occupies and activates an LCR that regulates the BCL6 proto-oncogene and is uniquely required by normal and malignant GC B cells. Mechanistically, through OCA-B-MED1 interactions, this complex is required for Mediator association with the BCL6 promoter. Densely tiled CRISPRi screening indicates that only LCR segments heavily bound by this ternary complex are essential for its function. Our results demonstrate how an intimately linked complex of lineage- and stage-specific factors converges on specific and highly essential enhancer elements to drive the function of a cell-type-defining LCR.
Journal: Molecular Cell PMID: 33232656 DOI: 10.1016/j.molcel.2020.10.036