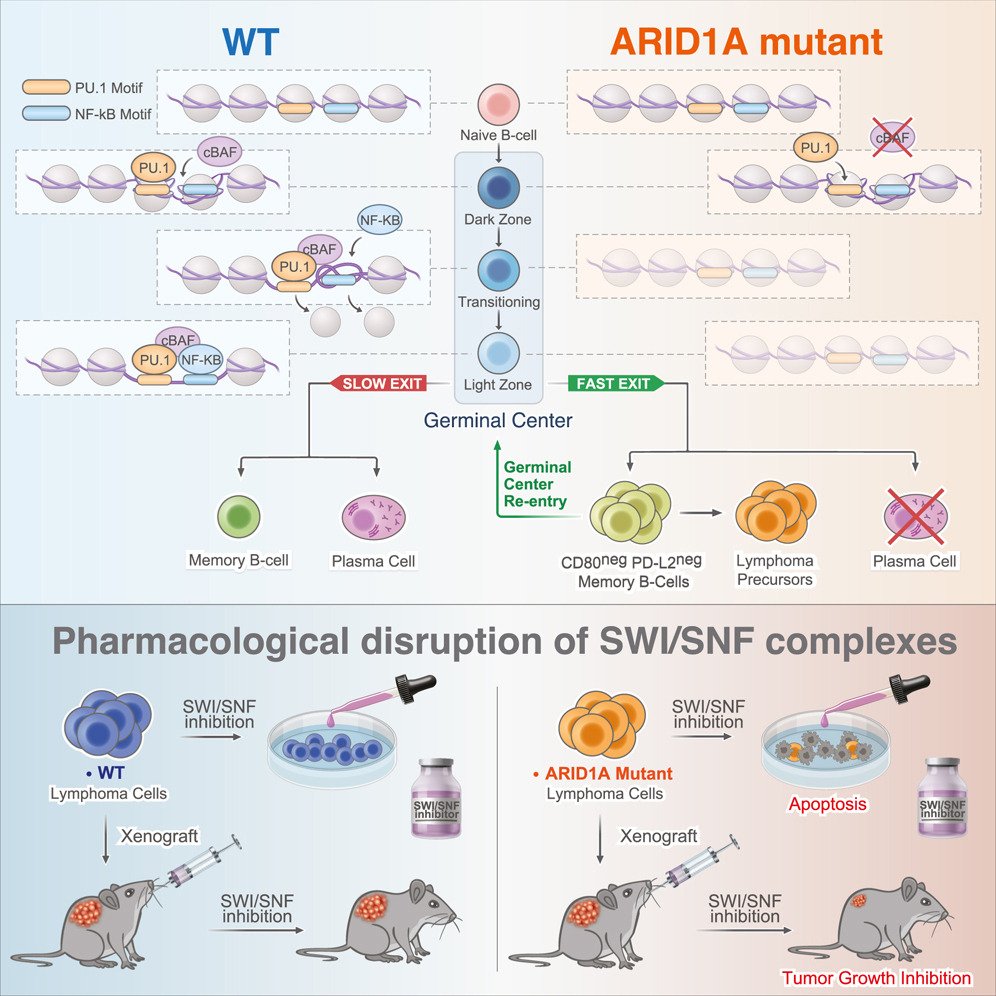
ARID1A orchestrates SWI/SNF-mediated sequential binding of transcription factors with ARID1A loss driving pre-memory B cell fate and lymphomagenesis.
ARID1A, a subunit of the canonical BAF nucleosome remodeling complex, is commonly mutated in lymphomas. We show that ARID1A orchestrates B cell fate during the germinal center (GC) response, facilitating cooperative and sequential binding of PU.1 and NF-kB at crucial genes for cytokine and CD40 signaling. The absence of ARID1A tilts GC cell fate toward immature IgM+CD80−PD-L2− memory B cells, known for their potential to re-enter new GCs. When combined with BCL2 oncogene, ARID1A haploinsufficiency hastens the progression of aggressive follicular lymphomas (FLs) in mice. Patients with FL with ARID1A-inactivating mutations preferentially display an immature memory B cell-like state with increased transformation risk to aggressive disease. These observations offer mechanistic understanding into the emergence of both indolent and aggressive ARID1A-mutant lymphomas through the formation of immature memory-like clonal precursors. Lastly, we demonstrate that ARID1A mutation induces synthetic lethality to SMARCA2/4 inhibition, paving the way for potential precision therapy for high-risk patients.
Journal: Cancer Cell PMID: N/A DOI: 10.1016/j.ccell.2024.02.010

TBL1XR1 Mutations Drive Extranodal Lymphoma by Inducing a Pro-tumorigenic Memory Fate
The most aggressive B cell lymphomas frequently manifest extranodal distribution and carry somatic mutations in the poorly characterized gene TBL1XR1. Here, we show that TBL1XR1 mutations skew the humoral immune response toward generating abnormal immature memory B cells (MB), while impairing plasma cell differentiation. At the molecular level, TBL1XR1 mutants co-opt SMRT/HDAC3 repressor complexes toward binding the MB cell transcription factor (TF) BACH2 at the expense of the germinal center (GC) TF BCL6, leading to pre-memory transcriptional reprogramming and cell-fate bias. Upon antigen recall, TBL1XR1 mutant MB cells fail to differentiate into plasma cells and instead preferentially reenter new GC reactions, providing evidence for a cyclic reentry lymphomagenesis mechanism. Ultimately, TBL1XR1 alterations lead to a striking extranodal immunoblastic lymphoma phenotype that mimics the human disease. Both human and murine lymphomas feature expanded MB-like cell populations, consistent with a MB-cell origin and delineating an unforeseen pathway for malignant transformation of the immune system.
Journal: Cell PMID: 32619424 DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2020.05.049

Non-oncogene Addiction to SIRT3 Plays a Critical Role in Lymphomagenesis
Diffuse large B cell lymphomas (DLBCLs) are genetically heterogeneous and highly proliferative neoplasms derived from germinal center (GC) B cells. Here, we show that DLBCLs are dependent on mitochondrial lysine deacetylase SIRT3 for proliferation, survival, self-renewal, and tumor growth in vivo regardless of disease subtype and genetics. SIRT3 knockout attenuated B cell lymphomagenesis in VavP-Bcl2 mice without affecting normal GC formation. Mechanistically, SIRT3 depletion impaired glutamine flux to the TCA cycle via glutamate dehydrogenase and reduction in acetyl-CoA pools, which in turn induce autophagy and cell death. We developed a mitochondrial-targeted class I sirtuin inhibitor, YC8-02, which phenocopied the effects of SIRT3 depletion and killed DLBCL cells. SIRT3 is thus a metabolic non-oncogene addiction and therapeutic target for DLBCLs.
Journal: Cancer Cell PMID: 31185214 DOI: 10.1016/j.ccell.2019.05.002
